The Dumbbell Around the World is a unique and powerful exercise that enhances shoulder flexibility, strengthens your deltoid muscles, and boosts rotator cuff stability. By guiding lightweight dumbbells through a slow, circular shoulder movement, you not only build strength but also improve your range of motion. This underrated yet effective move is perfect for athletes, beginners, and anyone recovering from minor shoulder stiffness.
It’s often used in shoulder warm-up routines, but it also fits well into any strength workout. The Dumbbell Around the World adds variety and challenge to your fitness routine, especially when aiming for total upper body control and balance. Let’s explore how this simple move delivers serious results.
What is the Dumbbell Around the World Exercise?
The Dumbbell Around the World is a circular motion shoulder exercise that strengthens your deltoid muscles while improving overall shoulder mobility. In this exercise, you rotate dumbbells in a full circle from the front of your body, up overhead, and down behind your back—then reverse it.
It’s often used as a shoulder warm-up routine, but it’s also powerful as a strength movement. This exercise challenges your rotator cuff stability, coordination, and core engagement during lifts, especially when done slowly and with controlled motion. Since it mirrors common overhead actions, this exercise is both functional and useful for daily movement strength.
Benefits of Dumbbell Around the World
ploring the diverse benefits of dumbbell around the world movements reveals a sophisticated path to elite fitness. Unlike standard linear presses, this circular motion demands exceptional shoulder flexibility to complete each sweeping repetition safely. By engaging the muscles through a 360-degree arc, you stimulate muscle hypertrophy in areas often missed by traditional routines. This unique exercise fosters incredible joint longevity by strengthening the delicate connective tissues surrounding the humerus. Furthermore, the constant tension required throughout the movement significantly enhances your scapular stability and overall postural control. Integrating this majestic sweep into your regimen transforms basic strength training into a comprehensive masterclass for a resilient, athletic physique.
Enhanced Shoulder Mobility and Joint Health
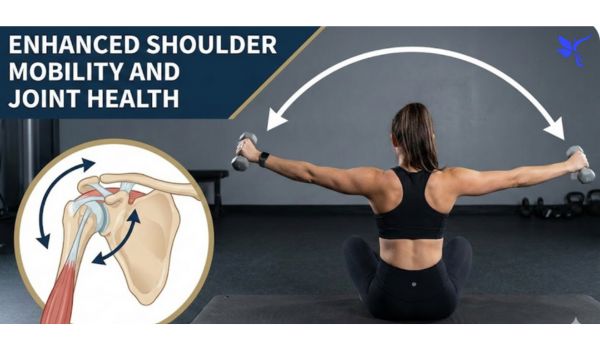
This exercise forces your arms through a massive 360-degree arc. This expansive path significantly improves your rotator cuff resilience over time. Most gym-goers neglect their full range of motion. By tracing this celestial circle, you lubricate the joints and prevent future nagging injuries.
Consistent practice builds a supple and buttery-smooth movement pattern. It stretches the chest while strengthening the rear structures simultaneously. Consequently, you develop a bulletproof upper body that handles heavy loads with ease. This is one of the premier benefits of dumbbell around the world sessions for longevity.
Scapular Stability and Postural Control
Your shoulder blades must dance in perfect rhythm during this lift. This specific requirement forces the seratus anterior to fire constantly. It is like a secret weapon for fixing rounded shoulders and slouching. You will walk taller and feel more anchored in every other compound movement.
Targeted Muscle Hypertrophy and Width
If you want that “capped” look, this movement is your best friend. It keeps the lateral deltoids under tension for a much longer duration than side raises. This prolonged stress triggers deep muscle growth. You are essentially sculpting your shoulders from every conceivable angle in a single set.
Furthermore, the secondary tension on the upper pectorals is quite profound. The benefits of dumbbell around the world include a more defined clavicular chest area. This creates a powerful and aesthetic “armor-plated” appearance. It fills in the gaps that traditional flat benching often leaves behind.
Core Bracing and Total Body Tension
As the weights move overhead, your trunk must fight to stay still. This engages the obliques and rectus abdominis with surprising intensity. You are getting a hidden ab workout while building massive shoulders. It turns a simple isolation drill into a full-body stabilization challenge.
| Feature | Physical Outcome | Training Impact |
| Circular Path | Better flexibility | Injury prevention |
| Continuous Tension | Faster muscle growth | Aesthetic “capped” look |
| Overhead Arch | Core engagement | Improved spinal health |
| Multi-planar Move | Joint longevity | Functional athleticism |
Maximizing Your Gains with Proper Form
The true benefits of dumbbell around the world appear when you slow down. Avoid using momentum to swing the weights like a pendulum. Instead, visualize your arms as the hands of a clock. Controlled tempo ensures every muscle fiber is recruited throughout the entire 360-degree revolution.
Using a lighter weight is often smarter for this specific technique. It allows you to focus on the mind-muscle connection without straining the delicate shoulder capsule. Precision beats ego every single time. Elevate your training by embracing the arc and watching your upper body transform.
Muscles Worked During Dumbbell Around the World
The primary muscles worked during dumbbell exercise routines like the “Around the World” include the anterior deltoids, lateral delts, and the pectoralis major. These movements demand high levels of scapular stability as the weights travel through a wide, circular arc. By engaging the rotator cuff and the upper trapezius, this exercise ensures your shoulder joints remain robust and mobile. Unlike static presses, this dynamic motion forces your core stabilizers to ignite to maintain a neutral spine. This holistic engagement creates a balanced, powerful upper body while fostering long-term athletic health and functional strength through consistent, controlled resistance training.
Primary Shoulder Targets: The Deltoid Trio

The anterior deltoids act as the primary engines during the initial upward phase of this wide, sweeping movement. These frontal muscles ignite to stabilize the weight as it traverses the frontal plane. You will feel a deep, satisfying burn as the fibers lengthen and contract rhythmically.
Simultaneously, the lateral delts govern the wide middle portion of the arc. This specific lateral engagement creates that coveted “capped” shoulder appearance many lifters desire. It is a seamless transition between the front and side segments of your shoulder anatomy during the full rotation.
The Posterior Deltoid Stabilization
While often overlooked, the posterior deltoid plays a vital role in controlling the descent of the dumbbells. This rear muscle group prevents the weights from drifting too far forward. It acts like a biological brake system to ensure your joints remain safe and perfectly aligned.
Synergistic Support: The Upper Chest and Back
Your pectoralis major serves as a powerful secondary driver when the dumbbells meet overhead. The clavicular head of the chest works hardest during the top half of the circle. This integration ensures your chest gains functional strength alongside your shoulders for a balanced look.
Furthermore, the trapezius muscles provide the necessary scaffolding to keep your shoulder blades tucked and secure. Without this upper back support, the weights would pull your posture out of alignment. Think of these muscles as the sturdy anchor for your moving limbs during the lift.
Rotator Cuff and Joint Health
Deep within the shoulder, the rotator cuff muscles work tirelessly to keep the humerus bone centered. These tiny stabilizers are crucial for long-term mobility and injury prevention. Strengthening them ensures your “greatest instrument”—your body—remains capable of high-performance training for years.
Core Engagement and Dynamic Stability
A steady trunk is essential because the rectus abdominis must counter the shifting center of gravity. As the weights move away from your midline, your core tightens to prevent arching. This internal bracing creates a solid foundation for every muscles worked during dumbbell exercise session.
Your obliques also kick in to manage the rotational forces acting on your spine. This lateral stability is what keeps you upright and prevents swaying during the peak of the arc. It turns a simple arm movement into a comprehensive, full-torso stabilization challenge.
| Muscle Group | Role in Movement | Benefit |
| Anterior Deltoids | Primary Mover | Improved pushing power |
| Lateral Deltoids | Width Specialist | Enhanced shoulder breadth |
| Pectoralis Major | Synergist | Upper chest definition |
| Trapezius | Stabilizer | Better postural control |
| Core Complex | Anchor | Spinal protection |
Pro Tip for Maximum Fiber Recruitment
To truly optimize the muscles worked during dumbbell exercise, maintain a slight bend in your elbows. This prevents joint strain while keeping the tension squarely on the muscle bellies. Slowly tracing a perfect circle maximizes time under tension for superior hypertrophy results.
How to Do Dumbbell Around the World Properly
rying to build a massive chest often feels like an uphill battle if you only stick to basic presses. Learning How to Do Dumbbell Around the World Properly is a game-changer for those seeking that “sweeping” muscular look. This unique isolation movement targets your torso through a circular path that most standard gym routines completely ignore. By lying in a supine position, you allow your shoulders to move through a wide arc that boosts upper body flexibility while placing a deep, productive stretch on the muscle fibers. Mastering this technique ensures your pectoralis major grows evenly, giving you both functional strength and a wider physical frame. It is the perfect tool for long-term joint health.
Setting Up for Maximum Success
To start, lie flat on a sturdy weight bench with your feet pressed hard into the floor. This provides the scapular stability you need to keep your shoulders safe while moving the weights. Hold your dumbbells at your hips with your palms facing up toward the ceiling.
Keep a very slight bend in your elbows so you don’t strain your joints. This setup is the secret to How to Do Dumbbell Around the World Properly because it aligns your muscles for the best possible pull. Avoid arching your back, as staying flat ensures the chest does all the heavy lifting.
Executing the Perfect Full Arc Motion

How to Do Dumbbell Around the World Properly? Move the dumbbells out to your sides in a wide, smooth semicircle until they meet above your head. This full arc motion should feel like you are making a snow angel with weights in your hands. Slow and steady wins the race here, never rush the movement.
Focus on the concentric phase as you bring the weights together, squeezing your chest muscles at the top. To keep the tension high, do not let the dumbbells actually touch each other. This constant work is what triggers the best results for hypertrophy training and muscle thickness.
Breathing and Eccentric Control
Take a deep breath in as you start the circle to expand your ribcage fully. As you lower the weights back to your hips, use slow eccentric control to resist the weight. This controlled lowering phase builds incredible muscular endurance and keeps your tendons healthy and strong.
Why This Move Beats Standard Presses
Most people focus on heavy weights, but How to Do Dumbbell Around the World Properly is about the quality of the movement. It serves as one of the best shoulder mobility exercises because it hits the joint from every angle. It also provides excellent rotator cuff strengthening which prevents future injuries.
If you have tight shoulders, this lift acts as a loaded stretch to improve your range of motion (ROM) over time. It helps clear out stiffness from heavy benching days. It’s a smart way to add variety to your chest and shoulder workout without needing complex machines.
Safety Tips and Form Fixes
How to do dumbbell around the world properly avoiding injury? Always prioritize shoulder impingement prevention by using a weight that feels manageable and smooth. If you feel a pinch in your joint, try doing dumbbell floor exercises for chest instead. The floor acts as a safety barrier so your arms don’t go too deep.
Make sure your palm orientation during lifts stays facing up throughout the entire circle. This keeps the shoulder joint in a “neutral” and safe position. Choosing the best weight for around the worlds usually means picking something much lighter than your standard chest fly weight.
Form Tips to Maximize Results
Keep your body still and your movements slow. Use a dumbbell control technique to avoid strain. If you move too quickly, you’ll lose the benefit of isolating the shoulder muscles. Focus on proper form and smooth transitions.
Don’t forget your breathing technique. Inhale as the dumbbells rise in front of you and exhale as they circle behind. This breathing rhythm helps you maintain energy and supports core engagement during lifts. Keep your neck relaxed and avoid shrugging to limit upper trapezius engagement.
Safety Tips & Precautions
If you’re new to shoulder mobility exercises, always begin with light dumbbell exercises. Going too heavy increases the risk of shoulder strain and poor form. Listen to your body. If you feel pinching or discomfort, stop immediately.
Also, make sure you’re warm before you start. Cold muscles are more prone to injury. Add some dynamic stretches or shoulder circles before jumping in. This supports your rotator cuff stability and protects the joint throughout the workout.
Coach’s Tips for Better Performance
A pro trainer would tell you: start small. Use this as a shoulder warm-up routine before heavy lifting. It’s the perfect prep for dumbbell shoulder workouts or pressing movements. The more you practice the circular motion shoulder exercise, the better your mobility and strength become.
To make this exercise more effective, combine it with shoulder rolls or deltoid strengthening moves. Don’t rush the reps. Perform each with intention and focus. This is where you’ll truly build control and progress.
Variations and Progressions
If you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to spice it up. Try using a weight plate instead of dumbbells to switch the load angle. Or do the movement lying down on a bench to activate the chest. That version adds variety and introduces exercise variations for upper body gains.
Advanced lifters can pause halfway through the circle or slow down the tempo. Another fun challenge? Add the Dumbbell Around the World at the end of your shoulder day to finish off with a serious burn. These tweaks keep your shoulder strengthening routine fresh and engaging.
Best Alternatives to Dumbbell Around the World
Can’t perform this move? No problem. Several dumbbell fly alternatives deliver similar results. You’ll still activate the deltoid muscles and improve shoulder flexibility.
Here are some top substitutes:
| Exercise | Benefit |
| Dumbbell Fly | Opens chest and shoulders |
| Incline Dumbbell Press | Builds upper chest and delts |
| Cable Crossover | Full range chest and shoulder work |
| Dumbbell Squeeze Press | Targets chest and inner shoulders |
| Resistance Band Lateral Raise | Great for rotator cuff work |
Each one trains similar muscles in a slightly different way. Add them to your routine regularly to keep your progress steady and break through training plateaus.
Sample Workouts That Include Dumbbell Around the World
You can include this move in warm-ups, supersets, or full upper-body splits. Here’s a quick sample routine:
Upper Body Day Example:
| Exercise | Sets | Reps |
| Dumbbell Around the World | 3 | 12 (each direction) |
| Dumbbell Shoulder Press | 3 | 10 |
| Dumbbell Lateral Raise | 3 | 12 |
| Incline Dumbbell Press | 3 | 10 |
| Cable Crossover | 3 | 15 |
This blend hits the front delts, side delts, and upper chest while improving shoulder joint stability and mobility.
Explore More Exercises by Muscle Group
Looking to train more efficiently? Target muscles by group. This helps balance your physique and prevents overtraining. Below are some movement suggestions:
| Muscle Group | Recommended Exercises |
| Chest | Incline Press, Squeeze Press, Machine Fly |
| Shoulders | Arnold Press, Front Raise, Lateral Raise |
| Arms | Hammer Curl, Skull Crushers, Triceps Dips |
To build a complete plan, pair these moves with Dumbbell Around the World at least twice a week.
Dumbbell Equipment & Recommendations
To get started, you need a quality set of lightweight dumbbells. For home workouts, adjustable dumbbells like Bowflex SelectTech or PowerBlock are excellent. If space is tight, choose hex dumbbells for easy storage.
Here’s a quick reference table:
| Brand | Type | Best For |
| Bowflex | Adjustable | Home gym users |
| CAP Barbell | Fixed-weight | Beginners & budget buyers |
| PowerBlock | Adjustable | Compact, strong design |
No matter your setup, the right gear helps you stay consistent and avoid injury.
Conclusion:
The Dumbbell Around the World may look simple, but it’s a game-changer for your shoulder health, mobility, and strength. It fits into almost any workout, enhances posture, and supports daily movement. With correct form, smart progressions, and the right tools, you can make this circular shoulder movement a staple in your training. Keep practicing, and your shoulders will thank you—both in the mirror and in daily life.
FAQ
What muscles do Dumbbell Around the World work?
It targets the deltoids, rotator cuff, and upper traps, mainly focusing on shoulder stability and mobility.
Are Dumbbells Around the World good?
Yes, they’re great for improving shoulder flexibility, control, and muscle activation using light weights.
Do Around the Worlds build muscle?
They help tone and strengthen shoulder muscles, but aren’t ideal for heavy mass-building.
Which muscles do Around the World work?
Primarily front and side deltoids, along with rotator cuff and trap muscles.
Are Around the Worlds effective?
Yes, especially for shoulder mobility, warm-ups, and injury prevention.
What is the hardest muscle to train in your body?
Calves are often the toughest due to constant daily use and slower muscle growth.

Muddasir Tahir is the founder and lead researcher at Lifestyle Dominates. With a strong passion for fitness and self-improvement, Muddasir spends his time studying human movement and high-performance habits.
His goal is to provide informational topics that are easy to understand and backed by careful research. Muddasir believes that everyone has the power to improve their lifestyle by mastering the right techniques.
When he isn’t researching new ways to help people dominate their lives, he is dedicated to building a community of like-minded individuals who strive for strength and a better mindset every day.
Hi there, I enjoy reading through your article post.
I wanted to write a little comment to support you.
Also visit my webpage: наращивание ссылочной массы
Thank You for your Compliment. Keep reading our blogs for useful content.
And also i would love to visit your web page too.
Very shortly this website will be famous among all blog viewers,
due to it’s fastidious content
Thank You very much for encouraging us in such a motivating way. Keep Visiting!